This song is about how we got here.
NB. Major spoilers ahead for Lady in the Dark (1944) and Phantom Thread (2017).
I first heard ‘My Ship’ several years ago – probably Nancy Wilson’s very beautiful big band recording from 1963, whose choppy instrumental introduction soon settles into golden plain sailing. Ira Gershwin’s lyrics fantasise luxuries arriving from far away, which are as nothing without the delivery of a soul-mate:
My ship has sails that are made of silk
The decks are trimmed with gold
And of jam and spice
There’s a paradise
In the hold
My ship’s aglow with a million pearls
And rubies fill each bin,
The sun sits high
In a sapphire sky
When my ship comes in
I can wait the years
Till it appears
One fine day one spring
But the pearls and such
They won’t mean much
If there’s missing just one thing
I do not care if that day arrives
That dream need never be
If the ship I sing doesn’t also bring
My own true love to me
Despite its sun, the song’s story reminded me of Christmas, most likely because of the carol ‘I Saw Three Ships (Come Sailing In)’. The nursery rhyme ‘I saw a ship a-sailing’, about a merchant vessel packed with treats and crewed by mice-sailors with “chains about their necks” was probably somewhere in my mind too: it appeared in ‘Ship in a Bottle’ (1974), the very first episode of Bagpuss.


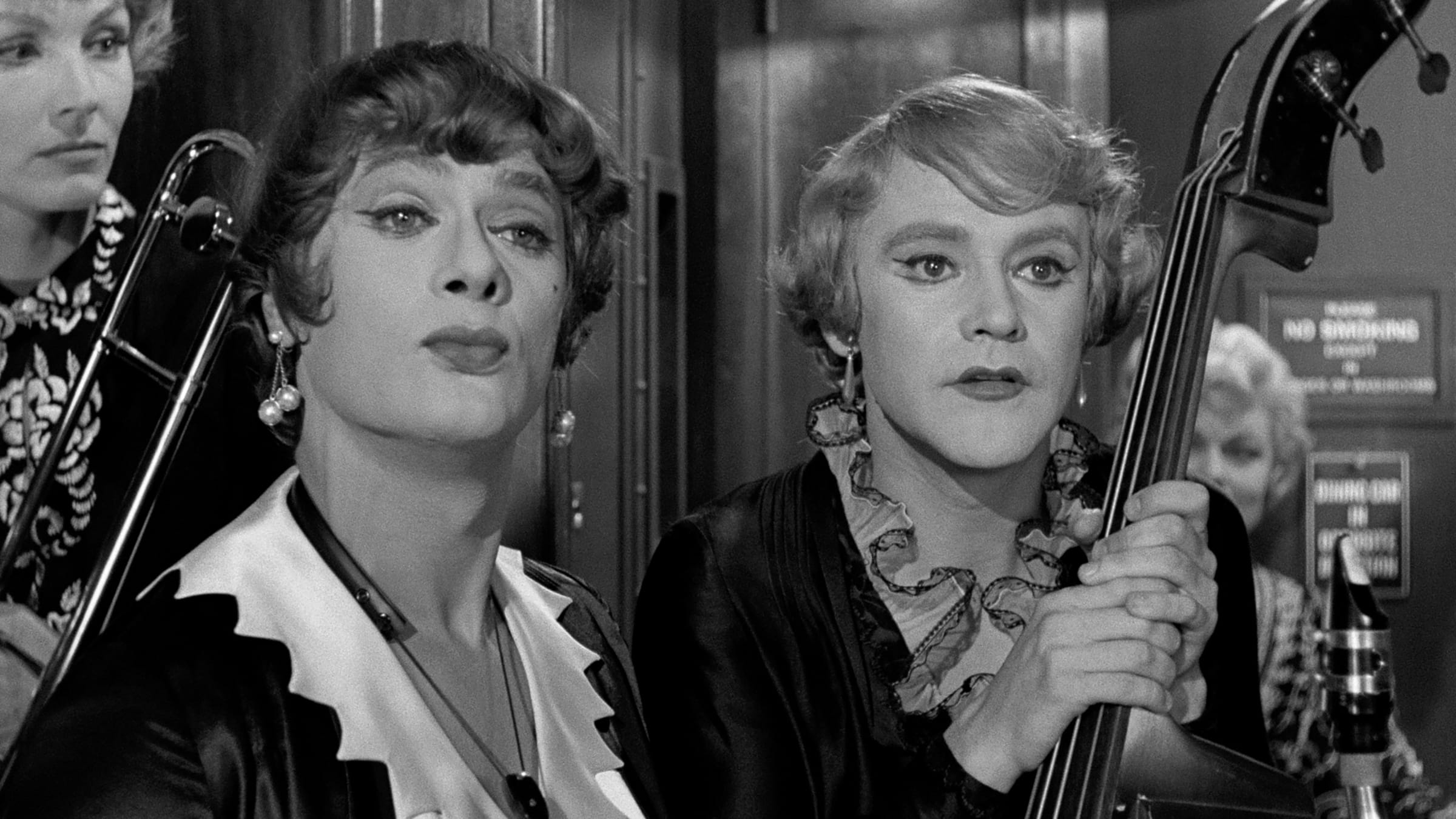
With Ira Gershwin, Kurt Weill composed the song for Moss Hart’s stage musical Lady in the Dark (1941). Liza Elliott, ambitious and successful editor of fashion magazine Allure, is in crisis. Her doctor recommends psychoanalysis. In the 1944 film dramatization – one of the highest grossing movies of the year – Liza (Ginger Rogers) finds herself humming a phrase from ‘My Ship’ repeatedly: an elusive echo of a repressed trauma. Psychoanalysis allows her to recall that as a young child she tried to perform the song at a family party. Her self-absorbed mother, preoccupied by male attention, is indifferent; the guests are thoughtlessly unkind, saying she is plain. As a child, Liza begins to hate her appearance. When her mother dies soon after, she is unable to grieve. She tries on her mother’s special blue dress, and her father chastises her angrily: a terrible rejection.
As Bruce McClung writes, ‘I saw a ship a-sailing’ is “the song’s predecessor”; further, “the gradual decoding of what ‘My Ship’ signifies sustains the drama, a process like the ‘Rosebud’ cipher in Citizen Kane“. In relation to the song’s image of a ship bearing bounties, Lady in the Dark is also, mindblowingly, ghosted by Shakespeare’s The Merchant of Venice (1596) – a play that dramatizes, amongst other things, “the new set of economic interactions that accompanied the birth of capitalism”. McClung notes that Moss Hart’s own experience of psychoanalysis was formative of the story, but that Freud’s ‘The Theme of the Three Caskets’ (1913) is what gives Lady in the Dark its structure. In the essay, Freud theorises the lottery for Portia’s hand in The Merchant of Venice: a choice between gold, silver and lead caskets, one of which contains her portrait. Like Bassanio, Hart has Liza select between three ‘caskets’ – publisher Kendall Nesbitt (Warner Baxter), actor Randy Curtis (Jon Hall), and her magazine’s advertising executive Charley Johnson (Ray Milland), who represent simplistically “the roles of father, lover, and husband”.
This film is a gorgeous waking nightmare, and watching it I was furious from beginning to end.
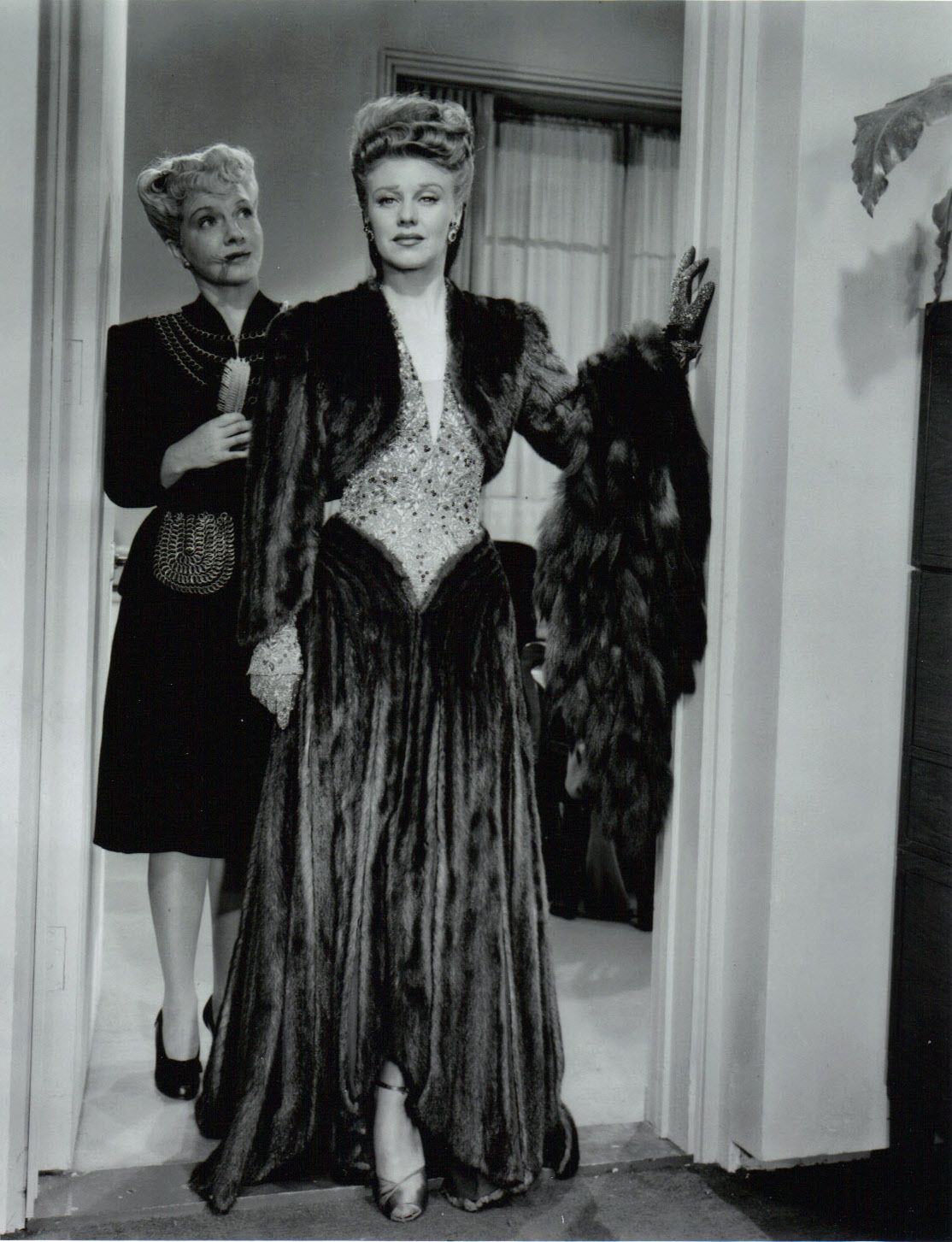
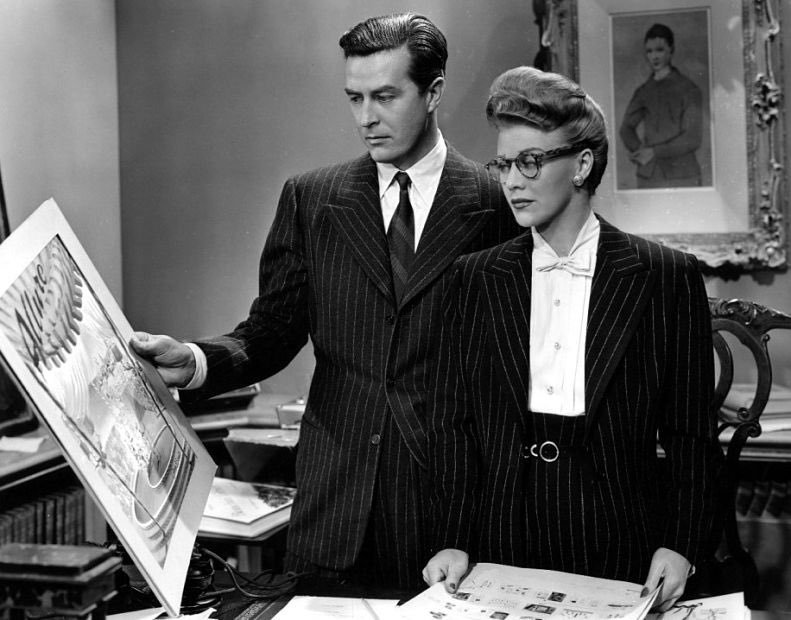


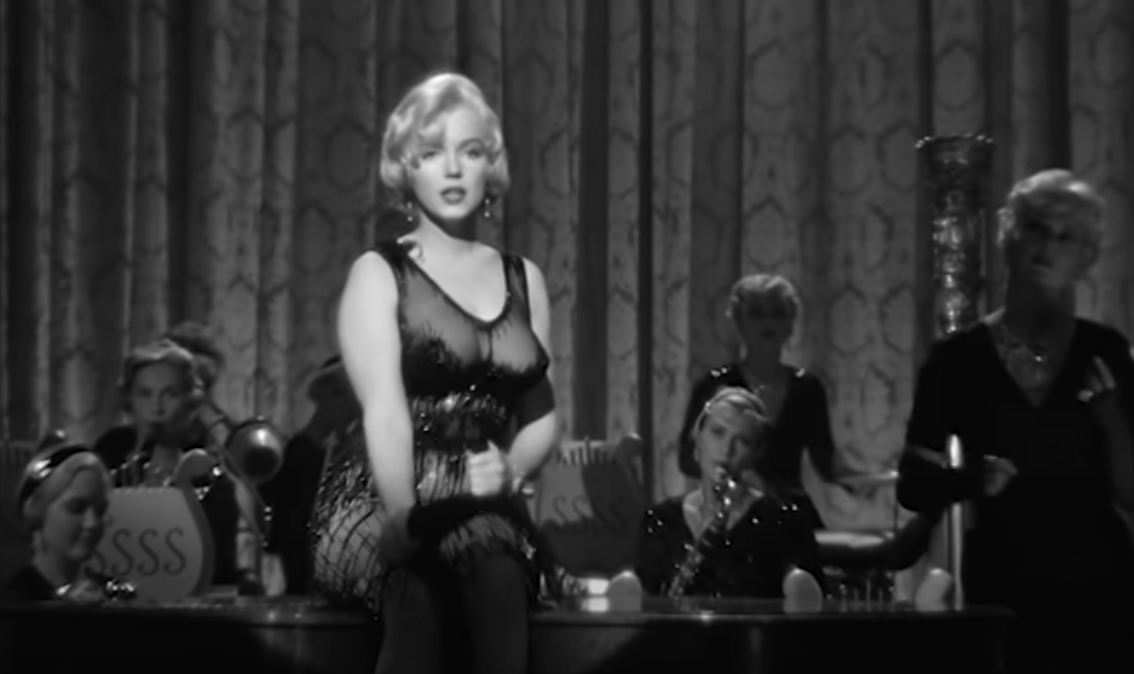
Amid the opulence of Allure‘s offices – the film’s lavish design and dream sequences subvert its maniacal heteronormativity – Charley attacks Liza continually, questioning her gender, sex life, and style, and brazenly declaring his desire for her job. When unusually she wears an evening gown on a date with Randy – a garment of sequin and mink that cost Paramount an eyewatering $35,000 dollars to produce – he jibes “you look wonderful – you actually look like a woman!” Her psychoanalyst Dr Brooks (Barry Sullivan) meanwhile proposes that, stemming from her childhood experiences, her distress lies with her reluctance to embrace femininity and “compete with other women”. Ignoring the injustices it so clearly lays out, the film egregiously weaponises psychoanalysis to confirm the “sex/gender system” and everything it supports. It ends with Liza agreeing to co-run the magazine with Charley, her literal tumble to the ground as he grabs her editorial chair for himself, and a kiss of unlikely passion between the two. This great review including on point picture captions (“Ray Milland is a shithead with a whip and Ginger Rogers is the lady in a cage in the circus dream”) fully has the measure of the film, as do these others on Letterboxd.
Paul Thomas Anderson’s extraordinary Phantom Thread (2017) includes ‘My Ship’. And Lady in the Dark seems to me to haunt the film in other ways, not least Freud’s essay.
At its conclusion Freud correlates the caskets to the mythological Fates (Moirai), the “three weaving goddesses who assign individual destinies to mortals at birth”, and thus to
the three inevitable relations that a man has with a woman – the woman who bears him, the woman who is his mate and the woman who destroys him; or that they are the three forms taken by the figure of the mother in the course of a man’s life – the mother herself, the beloved one who is chosen after her pattern, and lastly the Mother Earth who receives him once more. But it is in vain that an old man yearns for the love of a woman as he had it first from his mother; the third of the Fates alone, the silent Goddess of Death, will take him into her arms.
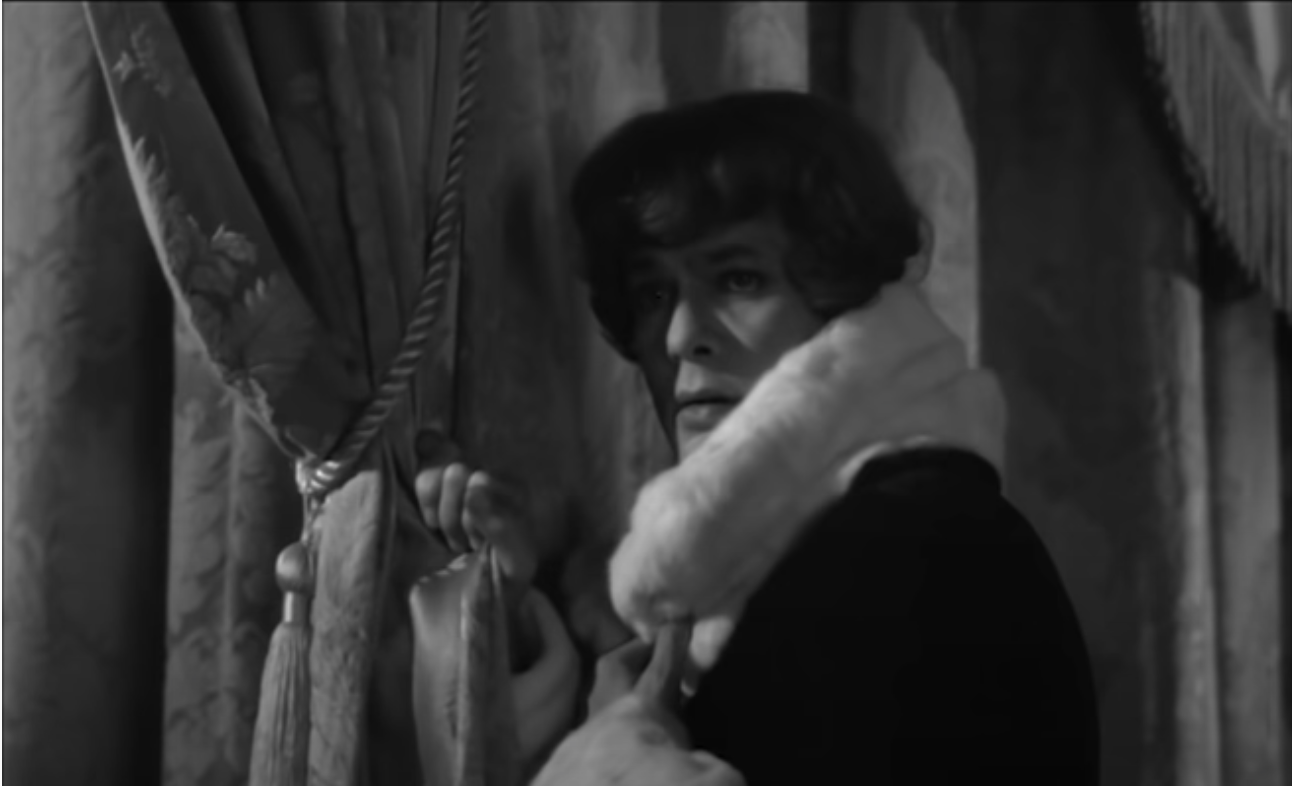
The relationship that Paul Thomas Anderson concocts between celebrated and exacting dressmaker Reynolds Woodcock (Daniel Day-Lewis) and his lover and model Alma (Vicky Krieps) attempts to have this cake and eat it. So consumed is Reynolds with his mother, and control over himself and his surroundings, that he cannot tolerate interruption or vulnerability, keeping his shrewd sister Cyril (Lesley Manville) close by as his safe companion. In these constrained, even hostile emotional circumstances, Alma (‘soul’) undertakes to derail his “games” by bringing him close to death: she feeds him poisonous mushrooms, then nurses him back to health, thereby impossibly occupying all three relations. This sadomasochistic gambit allows Reynolds to let go, to fall in love, to commit to her totally, and they have their own child. And so another cycle begins.


Oscar Peterson’s performance of ‘My Ship’ plays in the tearoom in which Woodcock first encounters Alma as a waitress, where he orders a ridiculous breakfast. Learning of Paul Thomas Anderson’s passion for big band jazz, I’m convinced that the narrative structure of Reynolds and Alma’s relationship is based on Nelson Riddle’s wonderful orchestral arrangement: brass and woodwind signal ‘watch out!’ before the song moves to surging strings, the solitary multiplicity of Peterson’s piano, and so on, periodically undercut by ambiguous, if not outrightly sinister harmonic choices. Key changes mark new phases, ascension to new heights. It’s almost unbearably poignant but also weirdly unserious somehow. It finishes with a steadying rallentando and fluttering flutes: a happy ending.
Aleksandar Hemon in the New Yorker concludes that Phantom Thread is “nothing if not propaganda for patriarchy”, and for sure I agree that it is in one sense a deep stitch-up, leaving little room for its women’s own desires beyond surviving these conditions, and doling out punishment for their perceived infractions. But like the stunning arrangement of ‘My Ship’ that it features, it is laced with compassionate unease, skewering power and fantasy with a delicate comic touch.










